#API Authentication
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Safeguarding Your Brand: The Power of Authentication
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, protecting your brand has never been more critical. With the rise of e-commerce and digital marketplaces, the threat of counterfeiting and unauthorized use of your brand is a constant concern. This blog explores the importance of authentication in brand protection, delving into its significance, strategies, and cutting-edge…

View On WordPress
#Anti-Counterfeiting#API Authentication#Authentication Methods#Brand Authentication#Digital Security
0 notes
Text
#qrevo.txt#i HATE tumblrs api docs I HATE ITTTT#it's covered in MISINFORMATION there's SO MANY WRONG INFO and the authentication guides are ASS#at least i did it....... i Understood.... i have the forbidden knowledge...
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Using Pages CMS for Static Site Content Management
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/using-pages-cms-for-static-site-content-management/
Using Pages CMS for Static Site Content Management
Friends, I’ve been on the hunt for a decent content management system for static sites for… well, about as long as we’ve all been calling them “static sites,” honestly.
I know, I know: there are a ton of content management system options available, and while I’ve tested several, none have really been the one, y’know? Weird pricing models, difficult customization, some even end up becoming a whole ‘nother thing to manage.
Also, I really enjoy building with site generators such as Astro or Eleventy, but pitching Markdown as the means of managing content is less-than-ideal for many “non-techie” folks.
A few expectations for content management systems might include:
Easy to use: The most important feature, why you might opt to use a content management system in the first place.
Minimal Requirements: Look, I’m just trying to update some HTML, I don’t want to think too much about database tables.
Collaboration: CMS tools work best when multiple contributors work together, contributors who probably don’t know Markdown or what GitHub is.
Customizable: No website is the same, so we’ll need to be able to make custom fields for different types of content.
Not a terribly long list of demands, I’d say; fairly reasonable, even. That’s why I was happy to discover Pages CMS.
According to its own home page, Pages CMS is the “The No-Hassle CMS for Static Site Generators,” and I’ll to attest to that. Pages CMS has largely been developed by a single developer, Ronan Berder, but is open source, and accepting pull requests over on GitHub.
Taking a lot of the “good parts” found in other CMS tools, and a single configuration file, Pages CMS combines things into a sleek user interface.
Pages CMS includes lots of options for customization, you can upload media, make editable files, and create entire collections of content. Also, content can have all sorts of different fields, check the docs for the full list of supported types, as well as completely custom fields.
There isn’t really a “back end” to worry about, as content is stored as flat files inside your git repository. Pages CMS provides folks the ability to manage the content within the repo, without needing to actually know how to use Git, and I think that’s neat.
User Authentication works two ways: contributors can log in using GitHub accounts, or contributors can be invited by email, where they’ll receive a password-less, “magic-link,” login URL. This is nice, as GitHub accounts are less common outside of the dev world, shocking, I know.
Oh, and Pages CMS has a very cheap barrier for entry, as it’s free to use.
Pages CMS and Astro content collections
I’ve created a repository on GitHub with Astro and Pages CMS using Astro’s default blog starter, and made it available publicly, so feel free to clone and follow along.
I’ve been a fan of Astro for a while, and Pages CMS works well alongside Astro’s content collection feature. Content collections make globs of data easily available throughout Astro, so you can hydrate content inside Astro pages. These globs of data can be from different sources, such as third-party APIs, but commonly as directories of Markdown files. Guess what Pages CMS is really good at? Managing directories of Markdown files!
Content collections are set up by a collections configuration file. Check out the src/content.config.ts file in the project, here we are defining a content collection named blog:
import glob from 'astro/loaders'; import defineCollection, z from 'astro:content'; const blog = defineCollection( // Load Markdown in the `src/content/blog/` directory. loader: glob( base: './src/content/blog', pattern: '**/*.md' ), // Type-check frontmatter using a schema schema: z.object( title: z.string(), description: z.string(), // Transform string to Date object pubDate: z.coerce.date(), updatedDate: z.coerce.date().optional(), heroImage: z.string().optional(), ), ); export const collections = blog ;
The blog content collection checks the /src/content/blog directory for files matching the **/*.md file type, the Markdown file format. The schema property is optional, however, Astro provides helpful type-checking functionality with Zod, ensuring data saved by Pages CMS works as expected in your Astro site.
Pages CMS Configuration
Alright, now that Astro knows where to look for blog content, let’s take a look at the Pages CMS configuration file, .pages.config.yml:
content: - name: blog label: Blog path: src/content/blog filename: 'year-month-day-fields.title.md' type: collection view: fields: [heroImage, title, pubDate] fields: - name: title label: Title type: string - name: description label: Description type: text - name: pubDate label: Publication Date type: date options: format: MM/dd/yyyy - name: updatedDate label: Last Updated Date type: date options: format: MM/dd/yyyy - name: heroImage label: Hero Image type: image - name: body label: Body type: rich-text - name: site-settings label: Site Settings path: src/config/site.json type: file fields: - name: title label: Website title type: string - name: description label: Website description type: string description: Will be used for any page with no description. - name: url label: Website URL type: string pattern: ^(https?://)?(www.)?[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]2,(/[^s]*)?$ - name: cover label: Preview image type: image description: Image used in the social preview on social networks (e.g. Facebook, Twitter...) media: input: public/media output: /media
There is a lot going on in there, but inside the content section, let’s zoom in on the blog object.
- name: blog label: Blog path: src/content/blog filename: 'year-month-day-fields.title.md' type: collection view: fields: [heroImage, title, pubDate] fields: - name: title label: Title type: string - name: description label: Description type: text - name: pubDate label: Publication Date type: date options: format: MM/dd/yyyy - name: updatedDate label: Last Updated Date type: date options: format: MM/dd/yyyy - name: heroImage label: Hero Image type: image - name: body label: Body type: rich-text
We can point Pages CMS to the directory we want to save Markdown files using the path property, matching it up to the /src/content/blog/ location Astro looks for content.
path: src/content/blog
For the filename we can provide a pattern template to use when Pages CMS saves the file to the content collection directory. In this case, it’s using the file date’s year, month, and day, as well as the blog item’s title, by using fields.title to reference the title field. The filename can be customized in many different ways, to fit your scenario.
filename: 'year-month-day-fields.title.md'
The type property tells Pages CMS that this is a collection of files, rather than a single editable file (we’ll get to that in a moment).
type: collection
In our Astro content collection configuration, we define our blog collection with the expectation that the files will contain a few bits of meta data such as: title, description, pubDate, and a few more properties.
We can mirror those requirements in our Pages CMS blog collection as fields. Each field can be customized for the type of data you’re looking to collect. Here, I’ve matched these fields up with the default Markdown frontmatter found in the Astro blog starter.
fields: - name: title label: Title type: string - name: description label: Description type: text - name: pubDate label: Publication Date type: date options: format: MM/dd/yyyy - name: updatedDate label: Last Updated Date type: date options: format: MM/dd/yyyy - name: heroImage label: Hero Image type: image - name: body label: Body type: rich-text
Now, every time we create a new blog item in Pages CMS, we’ll be able to fill out each of these fields, matching the expected schema for Astro.
Aside from collections of content, Pages CMS also lets you manage editable files, which is useful for a variety of things: site wide variables, feature flags, or even editable navigations.
Take a look at the site-settings object, here we are setting the type as file, and the path includes the filename site.json.
- name: site-settings label: Site Settings path: src/config/site.json type: file fields: - name: title label: Website title type: string - name: description label: Website description type: string description: Will be used for any page with no description. - name: url label: Website URL type: string pattern: ^(https?://)?(www.)?[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]2,(/[^s]*)?$ - name: cover label: Preview image type: image description: Image used in the social preview on social networks (e.g. Facebook, Twitter...)
The fields I’ve included are common site-wide settings, such as the site’s title, description, url, and cover image.
Speaking of images, we can tell Pages CMS where to store media such as images and video.
media: input: public/media output: /media
The input property explains where to store the files, in the /public/media directory within our project.
The output property is a helpful little feature that conveniently replaces the file path, specifically for tools that might require specific configuration. For example, Astro uses Vite under the hood, and Vite already knows about the public directory and complains if it’s included within file paths. Instead, we can set the output property so Pages CMS will only point image path locations starting at the inner /media directory instead.
To see what I mean, check out the test post in the src/content/blog/ folder:
--- title: 'Test Post' description: 'Here is a sample of some basic Markdown syntax that can be used when writing Markdown content in Astro.' pubDate: 05/03/2025 heroImage: '/media/blog-placeholder-1.jpg' ---
The heroImage now property properly points to /media/... instead of /public/media/....
As far as configurations are concerned, Pages CMS can be as simple or as complex as necessary. You can add as many collections or editable files as needed, as well as customize the fields for each type of content. This gives you a lot of flexibility to create sites!
Connecting to Pages CMS
Now that we have our Astro site set up, and a .pages.config.yml file, we can connect our site to the Pages CMS online app. As the developer who controls the repository, browse to https://app.pagescms.org/ and sign in using your GitHub account.
You should be presented with some questions about permissions, you may need to choose between giving access to all repositories or specific ones. Personally, I chose to only give access to a single repository, which in this case is my astro-pages-cms-template repo.
After providing access to the repo, head on back to the Pages CMS application, where you’ll see your project listed under the “Open a Project” headline.
Clicking the open link will take you into the website’s dashboard, where we’ll be able to make updates to our site.
Creating content
Taking a look at our site’s dashboard, we’ll see a navigation on the left side, with some familiar things.
Blog is the collection we set up inside the .pages.config.yml file, this will be where we we can add new entries to the blog.
Site Settings is the editable file we are using to make changes to site-wide variables.
Media is where our images and other content will live.
Settings is a spot where we’ll be able to edit our .pages.config.yml file directly.
Collaborators allows us to invite other folks to contribute content to the site.
We can create a new blog post by clicking the Add Entry button in the top right
Here we can fill out all the fields for our blog content, then hit the Save button.
After saving, Pages CMS will create the Markdown file, store the file in the proper directory, and automatically commit the changes to our repository. This is how Pages CMS helps us manage our content without needing to use git directly.
Automatically deploying
The only thing left to do is set up automated deployments through the service provider of your choice. Astro has integrations with providers like Netlify, Cloudflare Pages, and Vercel, but can be hosted anywhere you can run node applications.
Astro is typically very fast to build (thanks to Vite), so while site updates won’t be instant, they will still be fairly quick to deploy. If your site is set up to use Astro’s server-side rendering capabilities, rather than a completely static site, the changes might be much faster to deploy.
Wrapping up
Using a template as reference, we checked out how Astro content collections work alongside Pages CMS. We also learned how to connect our project repository to the Pages CMS app, and how to make content updates through the dashboard. Finally, if you are able, don’t forget to set up an automated deployment, so content publishes quickly.
#2025#Accounts#ADD#APIs#app#applications#Articles#astro#authentication#barrier#Blog#Building#clone#cloudflare#CMS#Collaboration#Collections#content#content management#content management systems#custom fields#dashboard#data#Database#deploying#deployment#Developer#easy#email#Facebook
0 notes
Text
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow applications to communicate with each other. Laravel provides multiple ways to build APIs, and Sanctum is the most efficient method for token-based authentication. In this tutorial, we’ll build a secure REST API in Laravel 12 using Sanctum with authentication, CRUD operations, and middleware protection.
#Laravel12#RESTAPI#Sanctum#Laravel#APIIntegration#LaravelSanctum#WebDevelopment#APIAuthentication#LaravelAPI#BackendDevelopment#LaravelApp#LaravelTutorial#PHP#LaravelSecurity#LaravelDevelopment#TokenAuthentication#API#RESTfulAPI#LaravelProjects#Authentication#APIRequests#SanctumAuthentication#WebAppDevelopment#LaravelBestPractices#LaravelAuth#APIFeatures#FullStackDevelopment
0 notes
Text
#CodeIgniter App#Web Application Development#Backend Development#REST API with CodeIgniter#PHP MVC#CRUD Operations#CodeIgniter Authentication#CodeIgniter Form Validation
0 notes
Text
Power Your Apps with Twilio SMS Messaging Solutions
Twilio SMS Messaging enables developers to send fast, secure, and scalable text messages globally. From customer alerts to two-factor authentication, integrate SMS into your apps effortlessly using Twilio’s robust API. Enhance user engagement with reliable and real-time communication tools.
#twilio sms#twilio development services#authentication#sms#api integration#twilio messaging services
0 notes
Text
Lazy Loading Page Speed Optimization: Efficient Practices & Tips

Key Takeaways
Lazy loading can significantly improve page speed by loading only necessary content initially, reducing initial load times.
Implementing lazy loading can save bandwidth, which is crucial for users on limited data plans.
This technique enhances user experience by ensuring faster interactions and smoother scrolling.
SEO can benefit from lazy loading as search engines prefer faster websites, potentially improving rankings.
To effectively implement lazy loading, use browser-native features and ensure compatibility across different devices.
Enhancing Web Performance with Lazy Loading
In today's fast-paced digital world, web performance is more critical than ever. Slow websites can drive users away, impacting engagement and conversions. One powerful technique to boost performance is lazy loading. By understanding and implementing lazy loading, you can optimize your website's speed and efficiency, keeping your visitors engaged and satisfied.
Understanding the Need for Speed
Users expect websites to load quickly and efficiently.
Slow loading times can lead to higher bounce rates.
Improved speed enhances user satisfaction and retention.
Most importantly, speed is not just a luxury; it's a necessity. Users are increasingly impatient, and a delay of even a few seconds can cause them to abandon your site. Therefore, ensuring that your site loads swiftly is crucial for maintaining user interest and engagement.
Lazy loading offers a solution by optimizing the loading process. Instead of loading every element of a page at once, lazy loading prioritizes essential content and defers non-essential elements. This approach can make a dramatic difference in how quickly your site feels to users.
Lazy Loading: A Game Changer for Web Efficiency
Lazy loading is more than just a buzzword; it's a transformative technique for web optimization. By deferring the loading of non-essential elements, such as images and videos, until they are needed, lazy loading reduces the initial load time of a webpage.
Images and videos load only when they enter the viewport.
Reduces server requests, enhancing page speed.
Particularly beneficial for mobile users with limited bandwidth.
Besides that, lazy loading helps in conserving resources, which is particularly beneficial for mobile users who might be on limited data plans. By only loading what's necessary, users experience faster interactions and smoother scrolling, which can significantly improve their overall experience.
Eager Loading: When Immediate Isn't Ideal
Eager loading, the opposite of lazy loading, involves loading all page elements at once. While this approach might seem straightforward, it can lead to longer initial load times, especially on content-heavy pages. Therefore, eager loading is not always the best choice, particularly when dealing with large images or videos.
Lazy loading, on the other hand, ensures that your website delivers essential content swiftly, making it an ideal choice for optimizing page speed and improving user experience.
Benefits of Lazy Loading
Lazy loading isn't just about speed; it's about creating a seamless and efficient user experience. Let's delve into the various benefits it offers.
Faster Initial Load Times
By loading only the necessary elements initially, lazy loading significantly reduces the time it takes for a page to become interactive. Users can start engaging with the content almost immediately, without waiting for all elements to load.
This immediate engagement is crucial in retaining user interest. For instance, if your homepage loads quickly, users are more likely to explore further, increasing the chances of conversion.
Additionally, faster load times can have a positive impact on your website's bounce rate. Users are less likely to leave if they don't have to wait for content to load, which can improve your site's overall performance metrics.
Loading Images Efficiently
Images often account for the majority of a webpage's load time. By implementing lazy loading for images, you can significantly improve your page speed. This involves loading images only when they are about to enter the viewport. As a result, users won't have to wait for all images to load before they can interact with your content.
To do this effectively, you can use the loading="lazy" attribute in your image tags. This attribute tells the browser to defer loading the image until it is close to being visible. Additionally, consider using responsive image techniques to serve different image sizes based on the user's device, further optimizing load times.
Handling Videos and Media Content
Videos and other media content can be resource-intensive, causing significant delays in load times if not managed properly. Lazy loading can also be applied to these elements. By embedding videos with lazy loading techniques, you ensure they only load when a user scrolls to them.
For example, instead of directly embedding a video, use a thumbnail image with a play button overlay. When the user clicks the play button, the video loads and plays. This not only saves bandwidth but also improves the initial loading speed of the page.
JavaScript and CSS Deferred Loading
JavaScript and CSS files are essential for modern web applications, but they can also be a bottleneck if not handled correctly. Lazy loading these resources involves deferring their loading until they are needed. This can be achieved using the defer and async attributes for JavaScript files.
The defer attribute ensures that the script is executed after the HTML document has been parsed, while the async attribute allows the script to be executed as soon as it's available. For CSS, consider using media queries to load stylesheets conditionally based on the user's device or viewport size.
Tips for Optimizing Lazy Loading
Implementing lazy loading is just the beginning. To truly optimize your website's performance, follow these additional tips and best practices.
Use Browser Native Features
Modern browsers offer native support for lazy loading, making it easier than ever to implement this technique. By using native features, you can ensure compatibility and reduce the need for third-party libraries, which can add unnecessary overhead.
To take advantage of these features, simply add the loading="lazy" attribute to your image and iframe tags. This simple addition can have a significant impact on your page speed, especially for image-heavy sites.
Besides, using native features ensures that your site remains future-proof, as browsers continue to enhance their support for lazy loading and other performance optimizations.
Minimize Default Image Size
Before applying lazy loading, it's crucial to optimize your images for size. Large images can still slow down load times, even with lazy loading. Use image compression tools to reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality.
Optimize Animations
Animations can enhance user experience, but they can also impact performance if not optimized. Use CSS animations instead of JavaScript whenever possible, as they are more efficient and can be hardware-accelerated by the browser.
Ensure that animations are smooth and don't cause layout shifts, which can negatively affect user experience. Test your animations on different devices to ensure they perform well across the board.
Remember, the goal is to create a seamless experience for your users. By optimizing animations, you can enhance the visual appeal of your site without compromising performance.
Test Across Multiple Devices
It's essential to test your website on a variety of devices and screen sizes. What works well on a desktop might not perform the same on a mobile device. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze your site's performance and identify areas for improvement.
Regular testing ensures that your lazy loading implementation works as intended across different platforms, providing a consistent experience for all users.
Overcoming Common Lazy Loading Challenges
While lazy loading offers numerous benefits, it's not without its challenges. Addressing these issues ensures that your implementation is successful and doesn't negatively impact your site.
Dealing with SEO Concerns
Lazy loading can sometimes interfere with search engine indexing if not implemented correctly. To ensure your content is indexed, use server-side rendering or provide fallbacks for search engines that may not execute JavaScript. For more insights, check out how lazy loading decreases load time and increases engagement.
Ensure all critical content is available without JavaScript.
Use structured data to help search engines understand your content.
Regularly monitor your site's indexing status in Google Search Console.
These strategies help maintain your site's visibility in search engine results, ensuring that lazy loading doesn't negatively impact your SEO efforts.
Addressing Browser Compatibility Issues
While most modern browsers support lazy loading, some older versions may not. To ensure compatibility, consider using a polyfill or fallback solutions for browsers that don't support lazy loading natively.
By addressing these compatibility issues, you can provide a consistent experience for all users, regardless of their browser choice. Regularly updating your site and testing on different browsers can help you identify and resolve any issues that arise.
Troubleshooting Loading Delays
Even with lazy loading implemented, you might encounter loading delays. This often happens when elements are not optimized or when there are too many third-party scripts running on your site. To troubleshoot these issues, start by identifying the elements that are causing delays. Use tools like Google Chrome's Developer Tools to pinpoint these elements and analyze their loading times.
Once you've identified the culprits, consider compressing images, deferring non-essential scripts, and minimizing the use of third-party plugins. By doing so, you can significantly reduce loading times and improve the overall performance of your website.
The Future of Lazy Loading in Web Development
Lazy loading is set to become an integral part of web development as websites continue to grow in complexity and size. With the increasing demand for faster and more efficient websites, lazy loading offers a practical solution to enhance user experience without compromising on content richness.
"Lazy loading is not just a trend; it's a necessity for modern web development. As websites evolve, so do the techniques we use to optimize them."
As more developers recognize the benefits of lazy loading, we can expect to see advancements in browser support and new tools that make implementation even easier. This evolution will ensure that lazy loading remains a vital component of web optimization strategies.
Emerging Technologies that Support Lazy Loading
Several emerging technologies are poised to enhance lazy loading capabilities. For instance, progressive web apps (PWAs) and server-side rendering (SSR) can work alongside lazy loading to deliver content more efficiently. PWAs offer offline capabilities and faster load times, while SSR ensures that content is rendered on the server, reducing the load on the client's device.
Additionally, advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning could further optimize lazy loading by predicting user behavior and preloading content accordingly. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize how we approach web performance optimization.
The Growing Importance of Mobile Optimization
As mobile usage continues to rise, optimizing websites for mobile devices has become more critical than ever. Lazy loading plays a crucial role in this optimization by reducing data usage and improving load times on mobile networks.
By implementing lazy loading, you can ensure that your mobile users have a seamless experience, regardless of their network conditions. This is particularly important for users in regions with slower internet speeds, where every byte counts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lazy loading is a powerful tool, but it can also raise questions for those unfamiliar with its implementation. Here are some common questions and answers to help you better understand lazy loading and its impact on your website.
These insights will help you make informed decisions about implementing lazy loading on your site and address any concerns you may have.
"Lazy loading can seem daunting at first, but with the right guidance, it becomes an invaluable asset for web optimization."
What is lazy loading and how does it work?
Lazy loading is a technique that defers the loading of non-essential elements, such as images and videos, until they are needed. This reduces the initial load time of a webpage, allowing users to interact with the content more quickly. By only loading elements when they enter the viewport, lazy loading conserves resources and improves performance.
How does lazy loading affect page speed and SEO?
Lazy loading can significantly enhance page speed by reducing the number of elements that need to be loaded initially. This not only improves user experience but also positively impacts SEO. Search engines favor faster websites, which can lead to improved rankings.
However, it's essential to ensure that lazy loading is implemented correctly to avoid any negative impact on SEO. This includes providing fallbacks for search engines that may not execute JavaScript and ensuring that all critical content is accessible without JavaScript. For more insights, check out this beginner's guide to lazy loading.
By addressing these considerations, you can harness the benefits of lazy loading without compromising your site's visibility in search engine results.
"Faster websites are favored by both users and search engines, making lazy loading a win-win for performance and SEO."
Therefore, lazy loading is an effective strategy for enhancing both user experience and search engine rankings.
What types of content should be lazy loaded?
Lazy loading is particularly beneficial for large images, videos, and other media content that can slow down a webpage. By deferring these elements, you can ensure that users only load what they need, when they need it.
Additionally, lazy loading can be applied to JavaScript and CSS files, further optimizing load times. By prioritizing essential content and deferring non-essential elements, you can create a more efficient and user-friendly website.
Are there any drawbacks to implementing lazy loading?
While lazy loading offers numerous benefits, it does have some potential drawbacks. If not implemented correctly, it can interfere with search engine indexing and result in missing or delayed content. To mitigate these risks, ensure that your lazy loading implementation is compatible with search engines and provides fallbacks for non-JavaScript environments. For more insights, check out Boost Your Website Speed With Lazy Loading.
How do I verify if lazy loading is working on my site?
To verify that lazy loading is working, use browser developer tools to inspect the network activity. Check if images and other media elements are loading only when they enter the viewport. Additionally, tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can help you analyze your site's performance and confirm that lazy loading is functioning as intended.
By regularly monitoring your site's performance and addressing any issues that arise, you can ensure that lazy loading continues to enhance your website's speed and user experience.
#A/B testing strategies#abstract design#Adobe Sensei automation#affordable AI tools#AI capability experimentation#AI-driven design suggestions#AI-driven innovation#alternate reality game#API integration#Appointment booking#appointment cancellation policy#ARG#authentic partnership#automated resizing#background removal#behind-the-scenes content#Blue color scheme#budget-friendly design software#Canva free version#Canva Pro features#Client data protection#client feedback tools#Client testimonials#Cloud Libraries#community building#community engagement#community engagement platforms#content automation#Conversion tracking#cost-effective strategies
0 notes
Text
Django REST Framework: Authentication and Permissions
Secure Your Django API: Authentication and Permissions with DRF
Introduction Django REST Framework (DRF) is a powerful toolkit for building Web APIs in Django. One of its key features is the ability to handle authentication and permissions, ensuring that your API endpoints are secure and accessible only to authorized users. This article will guide you through setting up authentication and permissions in DRF, including examples and…
#custom permissions#Django API security#Django JWT integration#Django REST Framework#DRF authentication#Python web development#token-based authentication
0 notes
Text
How to Secure your API key in Postman
API “Application Programming Interface” is the bedrock of all system applications. Without an API it will be impossible for the backend logic of an application to communicate with the frontend. API also makes it possible for an application to make a call or send a request to another application. In this article, I will show you how to Configure Postman for a Secure API key Authentication. You can…

View On WordPress
#Api intergration#Api management#APIs#Backup Repository#code#environment#key#key authentication#postman#Repository#security#Windows 10#Windows Server
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Safety and Privacy in Background Checks with Authenticate

Businesses must make sure that their partners and employees are real in the fast-paced business world of today. This helps to create a secure and reliable work environment in addition to protecting the company's brand. This is the point at which authentication is useful.
At Authenticate, we provide businesses with excellent background verification services to assist them in verifying the identity of their partners and workers. The Identity Verification App, Background Check Criminal Record, Background Check API, and Check Website Authentication are some services we offer.
Businesses may verify the background information of their employees easily and affordably by using the API Identity Verification. Our API easily interacts with the systems you already have, making the verification process quick and easy. Credit checks, work histories, and much more are included in this service. Our cutting-edge technology guarantees dependable and accurate outcomes, assisting you in making knowledgeable hiring decisions.
Our Criminal History Background Check service is the ideal answer for businesses wishing to confirm the criminal background of their staff members. Since we know that a company's safety is of utmost importance, our extensive criminal background check encompasses both domestic and foreign databases. Each report is carefully examined by our team of professionals to ensure that the results are accurate and dependable.
It is now essential for businesses in the digital era to confirm the identities of their partners and personnel. It is exactly what our Identity Verification App helps you achieve. Our app makes it simple to verify someone's identity using document verification and facial recognition. As part of this service, you can be sure that nobody in your company is using stolen or false identities by having duplicates checked.
At Authenticate, we understand the importance of maintaining confidentiality and privacy while conducting background checks. That's why we have stringent security measures to ensure that all information remains secure and protected. We also comply with all data privacy laws to safeguard your company's reputation and assets. To learn more about our service give us a call at +1 833-283-7439 or visit:- www.authenticate.com!
#Identity Verification App#Irs Identity Verification#Check Website Authentication#Best Identity Verification API#Consent-Based Identity Verification#API For Background Checks
0 notes
Text
Wish me luck tomorrow with my exam

#as soon as i finish it im gonna erase it from my mind#I'm all alone this weekend#time to study hard and code until 3 am#also if i get nervous in the exam im gonna 'cheat'#im sorry i pay 10$ a month Im going to use it if I need to#but probably wont need it#i hope#symfony its easy just put some commands and import everything in order#but its just 2 points#the rest it's going to be API#im afraid of the authentication part but I have a couple of examples#so glhf#next is JS que 0 problemas#diseño va a poner ejercicios que 100% seguro estan en internet xq es mas vago ...#y despliegues el último y el unico para el que tengo que estudiar realmente y si en el ultimo casi penco pero también ese lo puso a mala lec#he#tag rant
1 note
·
View note
Text
The MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js) is a popular full-stack JavaScript framework for building modern web applications. This stack allows developers to use a single language (JavaScript) across both client-side and server-side code. If you're a MERN stack developer, mastering key tasks within each of these technologies is crucial for creating robust and scalable web applications.
In this guide, we'll walk through the 10 most important tasks every MERN stack developer should master, helping you build a strong foundation for web development.
#MERNStack#MongoDB#ExpressJS#React#NodeJS#FullStackDevelopment#WebDevelopment#FrontendDevelopment#BackendDevelopment#JavaScript#API#RESTAPI#CRUDOperations#ReactJS#StateManagement#MongoDBQueries#Authentication#Authorization#JWT#Git#GitHub#DevTools#DevOps#Testing#PerformanceOptimization#Security#VersionControl#Deployment#CI/CD#Docker
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Power of APIs: Becoming an API Intermediate
The world of software development is driven by connectivity and integration. APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, lie at the heart of this digital ecosystem. They enable different software systems to communicate and share data seamlessly. As you delve deeper into the world of APIs, you’ll embark on a journey from novice to API Intermediate, acquiring a formidable skill set that empowers…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
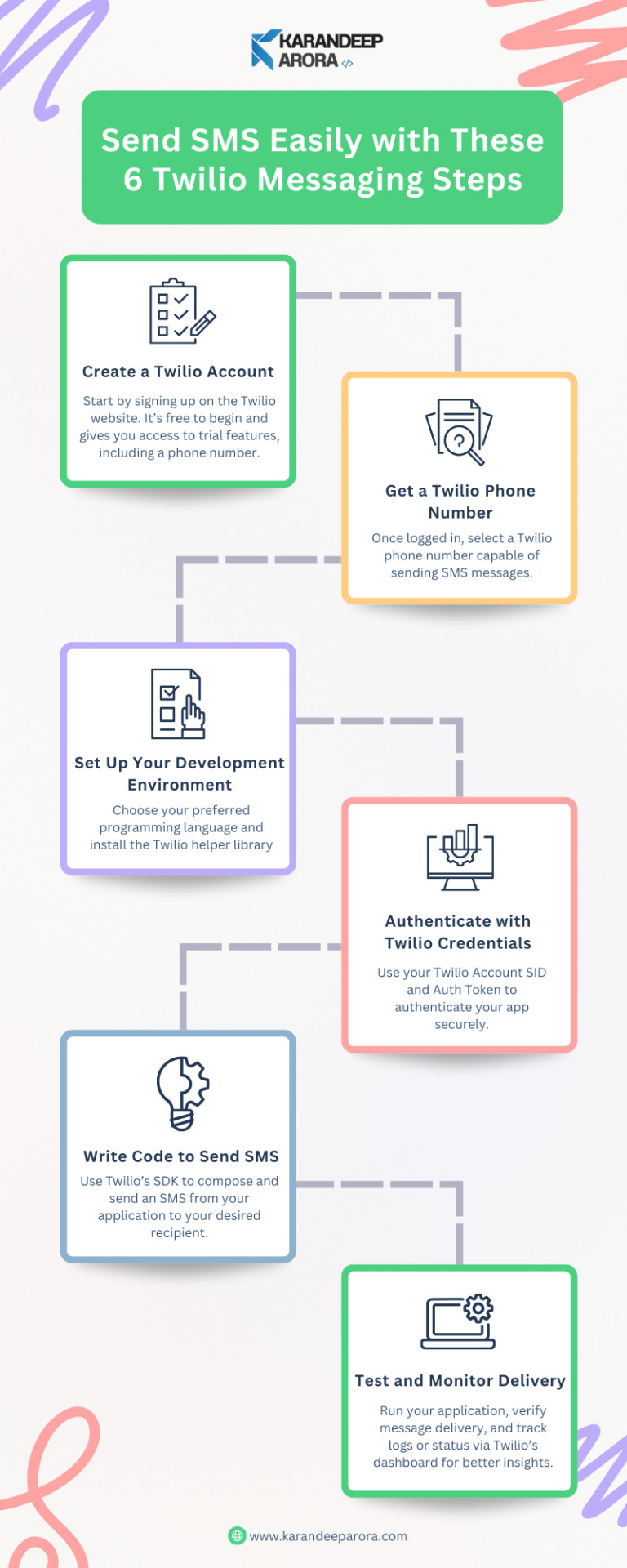
Effortlessly send and receive SMS with Twilio’s powerful API. Enable real-time notifications, two-factor authentication, and personalized messaging for your business. Scalable, reliable, and easy to integrate—Twilio SMS ensures seamless communication with customers worldwide. Get more information visit my website : www.karandeeparora.com
0 notes